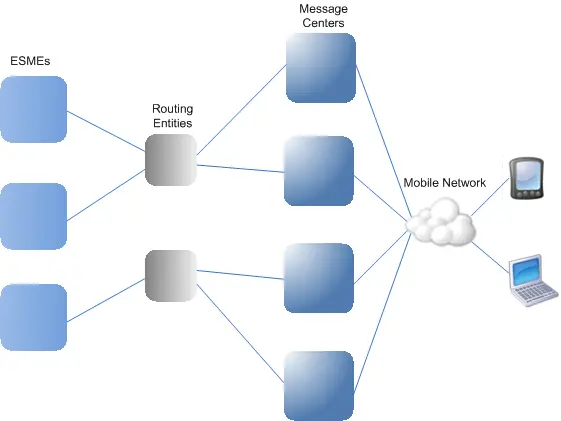
When it comes to telecom A2P (Application-to-Person) messaging, understanding the difference between zero hop and one hop connections can make a huge difference in how efficiently, cheaply, and reliably messages are delivered. Let’s break down what these terms mean and what they could mean for your business and customers.
What is A2P Messaging?
Before we dive into the details of zero hop and one hop connections, let’s cover the basics. A2P messaging refers to messages sent from an application to a person. Businesses use A2P messaging to communicate with customers, for things like OTPs (One-Time Passwords), alerts, notifications, promotions, and more.
Zero Hop Connections
A zero hop connection, or direct connection, means that the messaging service provider has a direct link to the mobile network operators (MNOs). In this setup, messages are sent straight from the service provider’s platform to the MNOs without any intermediaries.
Perks of Zero Hop Connections:
- Speed: No intermediaries mean faster message delivery, which is crucial for time-sensitive stuff like OTPs and alerts.
- Reliability: Direct connections are usually more reliable, with lower chances of message loss or delays.
- Security: Fewer risks of interception or tampering since there are no third parties in the mix.
- Transparency: Better control over message routing and delivery, leading to more accurate reporting and analytics.
Downsides of Zero Hop Connections:
- Cost: Setting up and maintaining direct connections with multiple MNOs can be pricey.
- Complexity: Managing relationships and technical integrations with multiple MNOs can be a hassle and resource-intensive.
One Hop Connections
A one hop connection involves one intermediary between the messaging service provider and the MNOs. This intermediary could be an SMS aggregator or another service provider that has direct connections with the MNOs.
Perks of One Hop Connections:
- Cost-Effective: Using an intermediary can save costs, as they already have established connections with multiple MNOs.
- Simplicity: Easier to manage since you only need to maintain a relationship with the intermediary, not multiple MNOs.
- Scalability: Easier to expand to new markets, as the intermediary often already has connections in those areas.
Downsides of One Hop Connections:
- Speed: An intermediary can introduce slight delays in message delivery.
- Reliability: More points of failure can lead to higher chances of message loss or delays.
- Transparency: Less control over the message routing process, which can impact the accuracy of reporting and delivery analytics.
- Security: More points where messages could be intercepted or tampered with.
Which Connection is Better?
Choosing between zero hop and one hop connections depends on what your business needs and prioritizes. For critical communications where speed, reliability, and security are key, zero hop connections are often the way to go, despite the higher cost and complexity. On the other hand, if you’re looking for cost-effective, scalable solutions with less management hassle, one hop connections might be a better fit.
Conclusion
Knowing the differences between zero hop and one hop connections is crucial for businesses using A2P messaging. Each option has its benefits and trade-offs, and the best choice depends on your business’s priorities regarding speed, reliability, security, cost, and scalability. As A2P messaging continues to evolve, staying informed about these options will help you make smart decisions to enhance your communication strategies.
Hope this gives you a clear and comprehensive overview of zero hop vs. one hop connections in telecom A2P messaging! If you’ve got any more questions or need further details, feel free to write to us on support@bloomwireglobal.com